Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
Vitamin D is an important nutrient that is vital to maintaining overall health. Unlike most vitamins, vitamin D works like a hormone because the body can synthesize it. This happens when the skin is exposed to sunlight. However, despite its importance, many people suffer from vitamin D deficiency without realizing it. This deficiency can lead to various health issues, including poor bone health and recurrent infections. This article will examine the common causes and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps the body absorb calcium, phosphate, and magnesium. These minerals are essential for building and maintaining strong bones. Vitamin D also supports brain, immune, and nervous system health. In addition, this vitamin influences insulin regulation and has anti-inflammatory properties. Primarily, there are two forms of vitamin D — D2 and D3. Vitamin D2 is obtained from plant sources and foods. However, vitamin D3 is obtained when the skin is exposed to early morning sun rays.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
There are many reasons people suffer from vitamin D deficiency. The causes include:
Limited Sunlight Exposure
Insufficient exposure to sunlight is one of the major causes of vitamin D deficiency. As stated earlier, the body produces this vitamin when the skin is exposed to sunlight. As such, people who mostly stay indoors or live in areas with limited sunlight are at a higher risk of being deficient. Factors like sunscreen and living in northern latitudes can cause reduced vitamin D synthesis.
Dark Skin
People with darker skin have a higher level of pigment called melanin. This pigment reduces the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. This means people with darker skin will need more sunlight exposure to produce the same amount of Vitamin D as someone with lighter skin. Consequently, Hispanic, South Asian, and African people are at a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Insufficient Diet
While sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, dietary intake also plays a role. Foods like fatty fish, dairy products, and egg yolks are rich in vitamin D. People who consume little or none of these are more susceptible to a deficiency. This is common in strict vegans, as plant-based foods contain lower amounts of vitamin D.
Obesity
Obesity can greatly contribute to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is fat-soluble, meaning it is stored in body fat. As such, it can get trapped in fat tissues in people with a higher fat percentage, making it less available to the body to use. Other causes of vitamin D deficiency are medical conditions, medications, and age.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency often goes unnoticed because symptoms can be mild or develop over time. However, insufficient vitamin D can have serious consequences for overall health. Some of the common symptoms include:
Bone and Back Pain
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, which is necessary for bone health. A deficiency can weaken bones, resulting in bone pain and brittle bones. Back pain, particularly in the lower back, can also be a symptom of insufficient vitamin D. The spine relies on calcium to maintain strength.
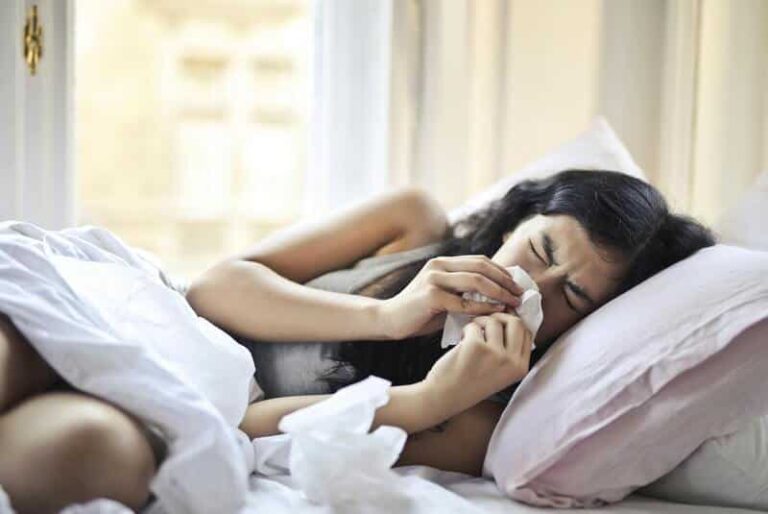
Frequent Infections or Illnesses
Vitamin D boosts immune function and helps the body fight off bacteria and viruses. Therefore, people with low vitamin D levels may have recurrent illnesses like colds, flu, and respiratory infections.
Muscle Weakness and Cramps
Vitamin D is essential for muscle function. People with a deficiency might notice muscle weakness, cramps, or aches. This is mostly noticeable in older adults who struggle to stand or walk.
Depression or Mood Changes
Vitamin D receptors are found in areas of the brain that regulate mood. So, a deficiency may lead to sadness, anxiety, or even depression. Some studies suggest that low vitamin D levels are associated with mood disorders. For example, seasonal affective disorder usually occurs during the darker months of the year.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread but often overlooked health issue that can lead to significant health problems if left untreated. Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms of a deficiency is important for early intervention. People at risk should increase sun exposure, eat vitamin D-rich foods, and take supplements. Maintaining sufficient levels of this nutrient is key to overall well-being.
Disclaimer: This article is intended simply to provide information. It does not replace the medical advice of a physician. Please speak with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.