Acne is one of the most common skin conditions worldwide. It affects millions of people regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. While it is commonly associated with adolescence, the condition can persist or develop in adulthood. It can vary from mild breakouts to more severe forms that can leave scars. Although it primarily affects the face, it can also appear on other body parts. Ultimately, understanding the causes, types, and treatment options is vital for managing the condition effectively.
What Is Acne?
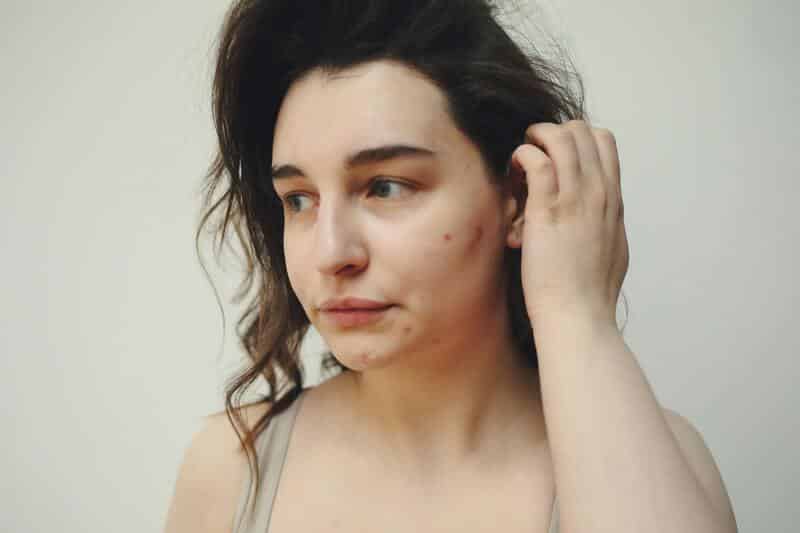

Acne is a condition that causes pimples. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. This leads to inflammation, blackheads, whiteheads, and even cysts. According to Pub Med, bacteria can play a role in its development. However, the severity of the condition depends on the strain of the bacteria. Research has also estimated that about 9.4 percent of people worldwide have acne. Also, according to the AAD, it is the most common skin condition in the U.S.
Types of Acne
Acne can manifest in different forms based on the severity of the blockage. People with the skin condition will notice a mix of pimple types. Here are the various types:
Whiteheads and Blackheads
Whiteheads usually form when a pore is completely blocked with dead skin cells or oil. They form small bumps under the skin’s surface, remaining flesh-colored. On the other hand, unlike whiteheads, blackheads form on the skin’s surface. They develop when a pore is partially blocked, allowing air to enter. Constant interaction with oxygen in the air gives the top of these pimples a darker appearance.
Papules and Pustules
Inflamed or infected hair follicles cause papules. This results in small, red, inflamed bumps. The bumps can be tender to touch but don’t contain pus. Similarly, pustules, often referred to as pimples, appear as small, red bumps. Unlike papules, they develop a white or yellow center filled with pus.
Nodules and Cysts
Nodules present as large and painful lumps. They develop deep beneath the skin’s surface when clogged pores cause severe inflammation. Due to their depth, this type of acne is harder to treat. Also, they are hard and don’t contain pus, unlike pustules. Similar to nodules, cysts are also quite large. They are the most severe form of the skin condition, characterized by pus-filled lesions. Cysts can be very painful and lead to scarring if not treated properly. They usually require medical attention and shouldn’t be self-treated.
Causes of Acne
Clogged hair follicles or pores by oil are the primary cause of the skin condition. In most cases, oil release and eventual blockage are caused by various factors. Let’s look at some of the significant causes of acne.
Hormonal Changes
Hormones play a significant role in acne development, especially during puberty. At this stage, there is an increase in androgen levels. This increase causes the oil glands to produce more sebum, resulting in pores getting clogged. Also, hormonal changes during pregnancy and the menstrual cycle can contribute to the condition in adults.
Genetics
Genetics can influence a person’s likelihood of developing acne. If your parents experienced acne, there is a possibility you might develop it as well. Heredity can affect how your skin responds to hormonal changes. Also, it can affect how much oil your skin produces and how easily pores can become blocked.
Bacteria
The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes is one of the causes of acne. It lives on the skin naturally but can get trapped in clogged pores. When this happens, it can multiply rapidly and lead to inflammation. Consequently, the inflammation can result in pimples, pustules, or even cysts.
Other causes of the condition include clogged pores from pollution and the use of comedogenic skincare products. In addition, studies suggest that sugary snacks, refined carbohydrates, and dairy products can cause it.
Treatment Options for Acne
Treating this skin condition effectively requires understanding its root cause. After identifying the cause, the right treatment method based on the severity of the condition is selected. Here are some of the best treatment options available:
Over-the-counter (OTC) Treatments
Moderate acne can be effectively managed with OTC products. Some remedies contain active ingredients like retinoids, salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, resorcinol, etc. These ingredients help clear clogged pores, killing bacteria and exfoliating the skin. It is advisable to start with the lowest strengths. This is because some remedies can cause skin irritation if misused.
Dermatological Procedures and Prescription Medication
For more severe forms of acne, dermatological procedures are often recommended. Some include facial chemical peels, drainage and extraction, and laser and light therapy. Also, dermatologists can prescribe stronger medication for persistent acne. Examples include topical retinoids, antibiotics, hormonal treatments, and oral retinoids.
Most importantly, lifestyle and skincare adjustments should be considered. Individuals should use non-comedogenic products and eat a balanced diet. They should also endeavor to stay hydrated and cleanse the skin gently to avoid irritation.
Conclusion
Acne can be frustrating, but with the proper treatment, it can be managed effectively. The importance of consulting a dermatologist can never be overemphasized. This is essential for finding a treatment plan that works for your skin type and condition. Once this is done, you’re one step away from achieving clearer and healthier skin.
Disclaimer: This article is intended simply to provide information. It does not replace the medical advice of a physician. Please speak with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.