You shouldn’t just protect your home from property damage and thieves, but also mold. You see, exposure to mold has led to chronic health issues including allergies and breathing difficulties. To combat this problem, you should control your home’s moisture levels to prevent and protect your health from any illnesses.
Understanding Mold Exposure
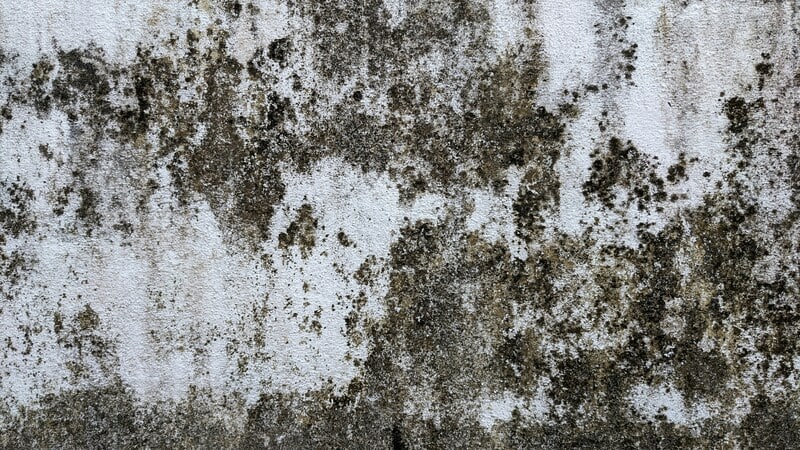
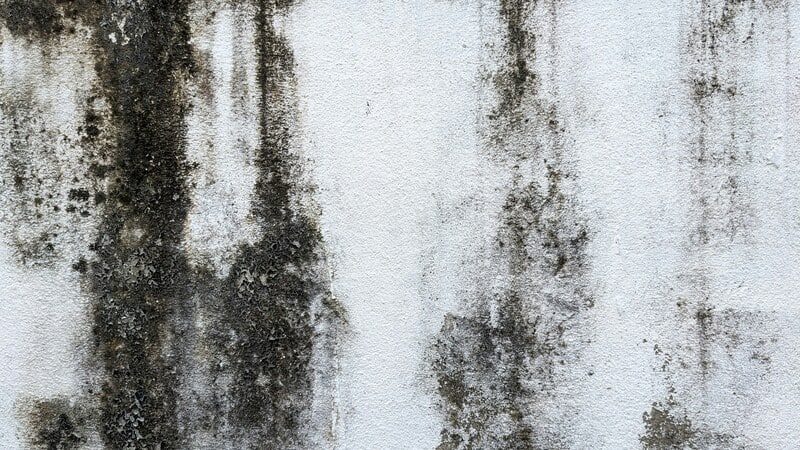
Typically, you can find mold growing on your clothes, walls, and other household objects, causing potential damage. As a type of fungus, it can grow both outdoors and indoors, affecting the air with the spores it produces. Even spaces where these spores cannot survive aren’t safe as they can be affected too. Mostly, these spores thrive in moist, warm conditions where they grow on any damp surface they land on including wood, fabric, glass, plaster, and paper. Once mold grows on these surfaces, it breaks down and digests the materials they contain.
Types of Mold
The mold types commonly found indoors include Aspergillus, penicillium, and cladosporium. Moreover, they’re most likely to be located in both warm and cool areas, appearing mostly on wood and fabric. Usually, you’ll find aspergillis growing on constructive material like drywall, dust, and even powdery food. In contrast, penicillium mostly grows on water-damaged objects or surfaces, appearing green or blue. Ultimately, however, molds come in various colors including black, white, greens, blues, and yellows. They may even share a similar appearance as stains or discolorations, and each type also has different textures, such as fuzzy, rough, and velvety.
Where to Find Mold Spores
Not only can mold grow anywhere outdoors and indoors but they’re invisible to the human eye. It can enter your home either by attaching to your clothing and other materials or through the air. On the bright side, it can only grow in certain conditions, including a landing somewhere surrounded by lots of moisture and proper nutrients. Indeed, you’re likely to find mold in spaces with poor air circulation, leaks, or condensation. Household materials such as ceiling and floor tiles, insulation, upholstery, and wooden surfaces are most susceptible to mold growth when wet.
Risk Factors of Mold Exposure
In particular, mold poses certain health risks if you struggle with a weakened immune system, allergies, or respiratory issues. While growing, it releases spores along with compounds and cells into the air, which may prove harmful. Following their release, these materials start to act like irritants, allergens, or even mycotoxins, possibly affecting any sensitivities you may have.
Like seasonal allergies, the symptoms of mold allergies are blocked and runny noses, sneezing, watery eyes, and itchy throat. If you struggle with asthma, exposure may increase your chances of getting an asthma attack. These health issues are the main reasons why you must manage your exposure to prevent them from happening.
Aspergillus

Specifically, aspergillus may cause a severe health condition called Aspergillosis. Particularly, if you have a weakened immune system or a pre-existing lung condition, you’re more likely to be affected. Although inhaling spores from Aspergillosis without getting sick is possible, you’re still at risk of experiencing severe reactions.
Mainly, there are various types of aspergillosis, including allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), which tends to impact your lungs, leading to shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. More than that, you may struggle with allergic aspergillus sinusitis, leading to headaches, nasal stuffiness, and a runny nose. You may develop aspergilloma, known as fungus balls, which may lead you to develop breathing difficulties or, in worse cases, coughing with blood. Comparatively, chronic pulmonary aspergillosis can cause coughing, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Mold Growth Prevention
To prevent mold growth indoors, you should control the moisture in your home and maintain a clean home. Another way to combat this growth, reduce the humidity in your household by keeping it well-ventilated. According to the Environment Protection Agency (EPA), indoor humidity levels should remain below 60%. Fixing leaks and using dehumidifiers in your home is one method to reduce humidity. Keeping your windows open for better air circulation and using extractor fans when baking or cooking can also help.
Final Thoughts
Although mold spores inhabit all indoor environments, they usually don’t affect you. However, gaining a compromised immune system may put you at risk of certain lung illnesses if you’re exposed to run or experience allergic reactions. For prevention or removal, you should look into specific cleaning methods to free your home of these pores. Any concerns you may have about mold-related health conditions can be remedied by consulting a healthcare professional for advice and treatment.
Disclaimer: This article is intended simply to provide information. It does not replace the medical advice of a physician or other medical professional. Please speak with your doctor or therapist if you have any questions or concerns.